Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the cardiovascular system – Heart.
The heart is a fist-sized vital organ that has one job: to pump blood. If one assumes an average heart rate of 75 beats per minute, a human heart would beat approximately 108,000 times in one day, more than 39 million times in one year, and nearly 3 billion times during a 75-year lifespan. At rest, each of the major pumping chambers of the heart ejects approximately 70 mL blood per contraction in an adult. This would be equal to 5.25 liters of blood per minute and approximately 14,000 liters per day. Over one year, that would equal 10,000,000 liters of blood sent through roughly 100,000 km of blood vessels. In order to understand how that happens, it is necessary to understand the anatomy and physiology of the heart.
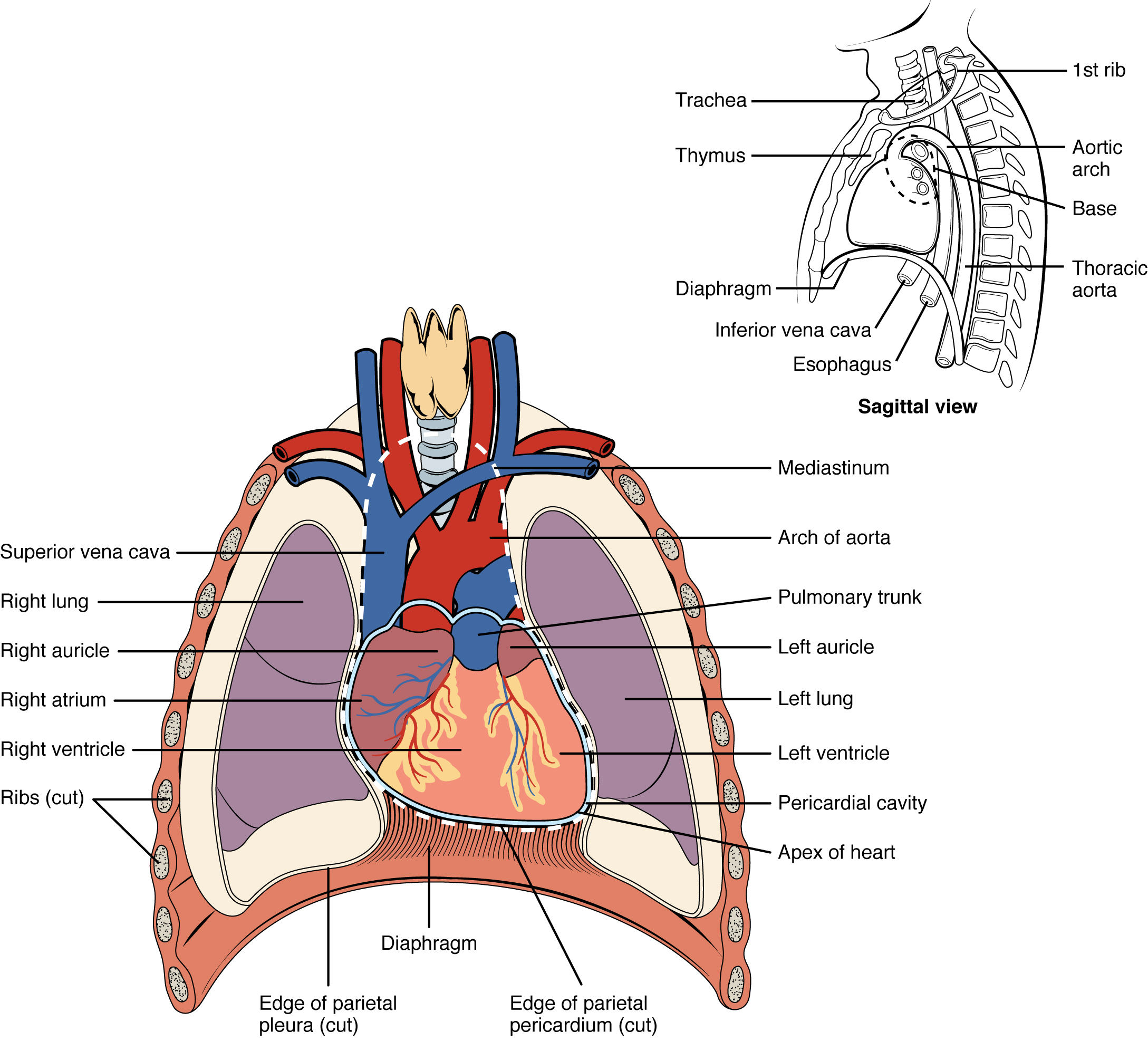
The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. Figure 9.1 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. Within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium, or pericardial sac, and sits in its own space called the pericardial cavity. The great vessels, which carry blood to and from the heart, are attached to the superior surface of the heart, which is called the base. The base of the heart is located at the level of the third costal cartilage. The inferior tip of the heart, the apex, lies just to the left of the sternum between the junction of the fourth and fifth ribs.

The heart and the roots of the great vessels are surrounded by a membrane known as the pericardium or pericardial sac. The pericardium consists of two distinct sub layers:
The walls of the heart consist of three layers:
 Layers of the Heart Wall. The pericardial membrane that surrounds the heart consists of three layers and the pericardial cavity. The heart wall also consists of three layers. The pericardial membrane and the heart wall share the epicardium." width="581" height="581" />
Layers of the Heart Wall. The pericardial membrane that surrounds the heart consists of three layers and the pericardial cavity. The heart wall also consists of three layers. The pericardial membrane and the heart wall share the epicardium." width="581" height="581" /> 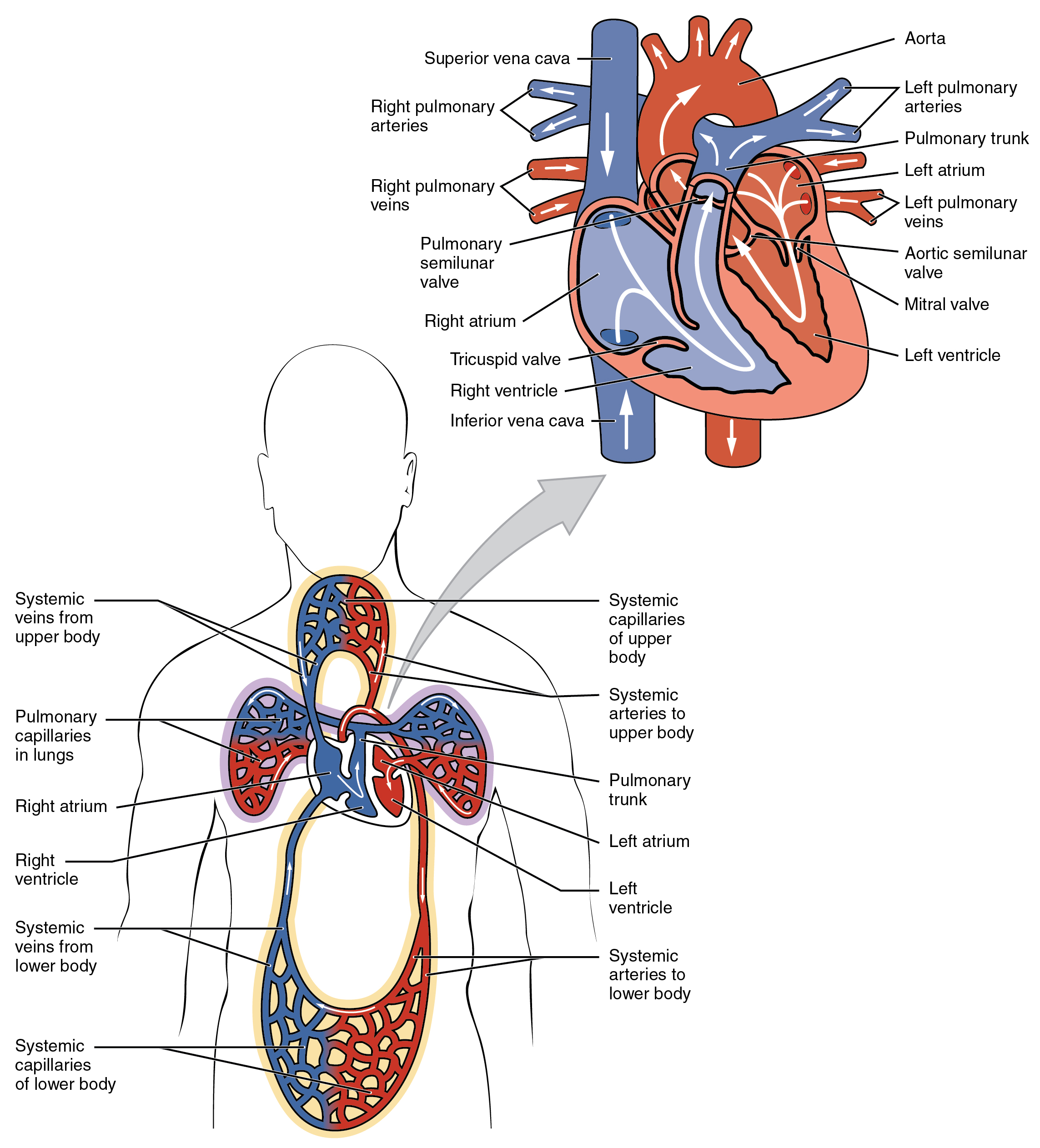
The process of pumping and circulating blood is active, coordinated and rhythmic. Each heartbeat represents one cycle of the heart receiving blood and ejecting blood.
Many terms and phrases related to the cardiovascular system- heart are abbreviated.
Learn these common abbreviations by expanding the list below.
The heart of a well-trained athlete can be considerably larger than the average person’s heart. This is because exercise results in an increase in muscle cells called hypertrophy . Hearts of athletes can pump blood more effectively at lower rates than those of non-athletes. However, when an enlarged heart is not the result of exercise, it may be due to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The cause of an abnormally enlarged heart muscle is unknown, but the condition is often undiagnosed and can cause sudden death in apparently otherwise healthy young people (Betts, et al., 2021).
Other types of cardiomyopathy include:
Cardiomyopathy may also be caused by myocardial infarctions, myocardial infections, pregnancy, alcohol or cocaine abuse, autoimmune and endocrine diseases. Because the myocardium is responsible for contracting and pumping blood, patients with cardiomyopathy experience impaired heart function which may lead to heart failure. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019). To learn more about cardiomyopathy visit the CDC’s cardiomyopathy web page.
Heart failure is defined as the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. It is also called congestive heart failure (CHF). This condition causes swelling in the lower extremities and shortness of breath, due to a buildup of fluid in the lungs. It may be caused by cardiomyopathy and it may lead to hypertension and heart valve disorders (Heart & Stroke, n.d.). To learn more, visit the Heart & Stroke’s congestive heart failure web page.
Do you remember the names and locations of the 4 heart valves?
The four heart valves open and close at specific times during the cardiac cycle, in order to ensure that blood flows in only one direction through the heart. This requires that these valves open and close completely. Infections such as rheumatic disease or bacterial endocarditis can affect the heart valves and result in scar tissue formation which interferes with valve function. Other causes of heart valve disease include: congenitally malformed valves, autoimmune diseases, and other cardiovascular diseases such as aortic aneurysms and atherosclerosis (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019a).
Heart valve disease may be asymptomatic, or cause dyspnea, arrhythmias, fatigue and other symptoms. It is often detected when a heart murmur is heard through a stethoscope (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019a).
An aneurysm is a defect in the wall of an artery in which the wall becomes thin and weak and starts to balloon out as blood pulses against the vessel wall. This can happen to any artery and even to the myocardial walls. Aneurysms sometimes occur in the portion of the aorta that is in the thorax (see Figure 9.4). If these aneurysms start to leak between layers of the vessel wall, the condition is known as aortic dissection. If an aortic or cardiac aneurysm bursts, there is sudden, massive internal bleeding (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019b).

People who smoke, have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and/or atherosclerosis have an increased risk of developing aneurysms. Having a family history of aneurysms or certain genetic diseases may also increase a person’s risk of developing an aneurysm.
Aneurysms are often asymptomatic and may be detected incidentally during diagnostic tests that are being done for other reasons. They are sometimes repaired surgically and sometimes treated with medications such as antihypertensives (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019b; Tittley, n.d.). Visit the Society for Vascular Surgery’s page on thoracic aortic aneurysms to learn more.
Fetal circulation is different from postnatal circulation. There are 2 extra openings in the fetal heart, the foramen ovale and the ductus arteriosus, which allow blood circulation that bypasses the immature fetal lungs. The fetal blood is reoxygenated by the mother’s lungs and transported between mother and fetus via the placenta. These two openings usually close around the time of birth (Betts, et al., 2021).
Septal defects are commonly first detected through auscultation. Unusual heart sounds may be detected because blood is not flowing and valves are not closing correctly. Medical imaging is ordered to confirm or rule out a diagnosis. In many cases, treatment may not be needed.

Coronary artery disease occurs when the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries obstructs the flow of blood and decreases compliance of the vessels. This condition is called atherosclerosis. As the disease progresses and coronary blood vessels become more and more narrow, cells of the myocardium become ischemic, which causes symptoms of angina pectoris, in some patients. If untreated, coronary artery disease can lead to MI.
The image below shows the blockage of coronary arteries on an angiogram (Betts, et al., 2021).
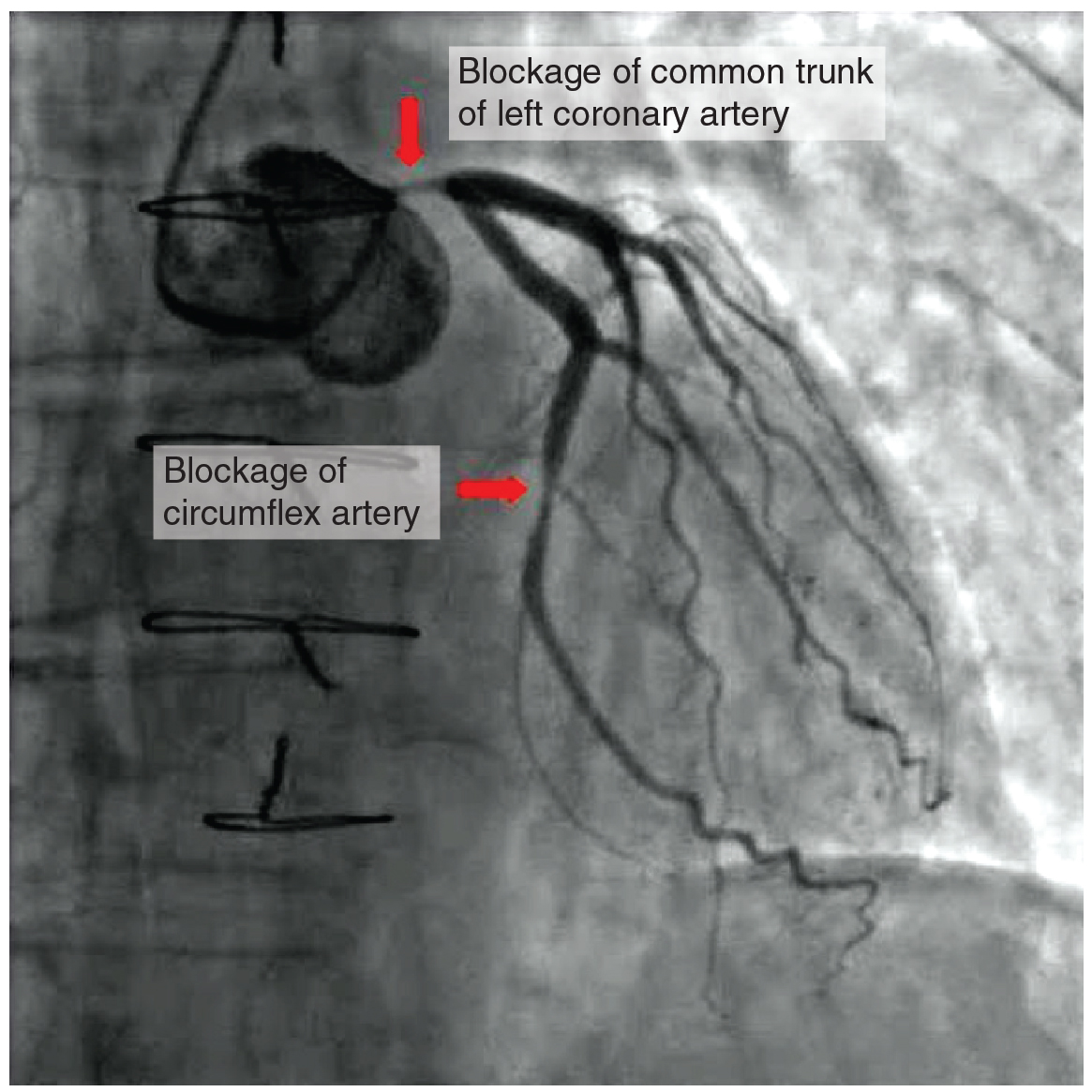
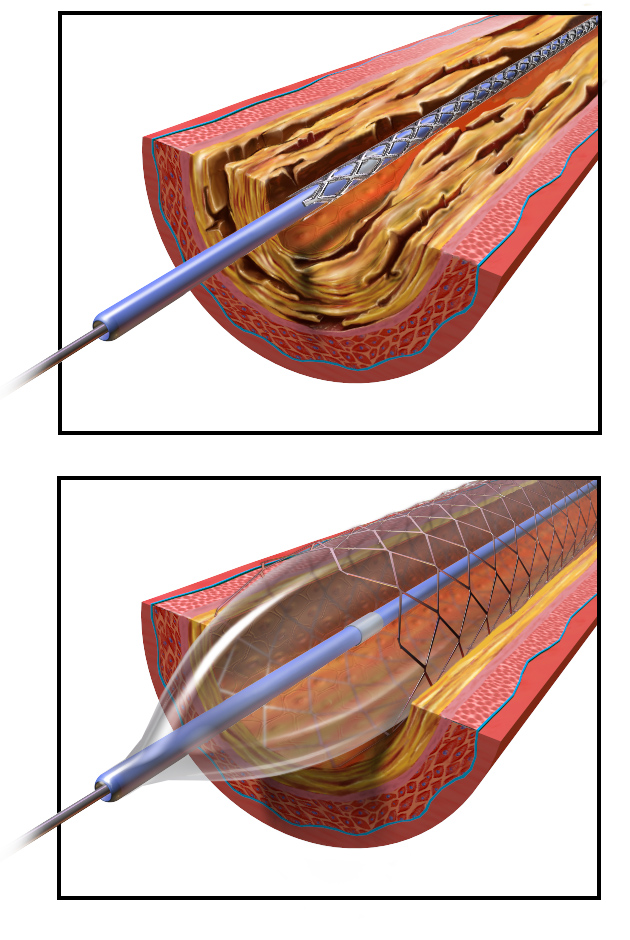
CAD is progressive and chronic. Risk factors include smoking, family history, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, high alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, stress, and hyperlipidemia. Treatments may include medication, changes to diet and exercise, angioplasty with a balloon catheter, insertion of a stent, or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) (Betts, et al., 2021).

Myocardial infarction (MI) is the medical term for a heart attack.
An MI normally results from a lack of blood flow to a region of the heart, resulting in death of the cardiac muscle cells. An MI often occurs when a coronary artery is blocked by the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque. It can also occur when a piece of an atherosclerotic plaque breaks off and travels through the coronary arterial system until it lodges in one of the smaller vessels. MIs may be triggered by excessive exercise, in which the partially occluded artery is no longer able to pump sufficient quantities of blood, or severe stress, which may induce spasm of the smooth muscle in the walls of the vessel (Betts, et al., 2021).
In the case of acute MI (AMI), there is often sudden pain beneath the sternum (retrosternal pain) called angina pectoris, often radiating down the left arm in males but not in female patients. Other common symptoms include dyspnea, palpitations, nausea and vomiting, diaphoresis, anxiety, and syncope. Many of the symptoms are shared with other medical conditions, including anxiety attacks and simple indigestion, so differential diagnosis is critical (Betts, et al., 2021).
An MI can be confirmed by examining the patient’s ECG.
Other diagnostic tests include:
MIs may induce dangerous heart rhythms and even cardiac arrest. Important risk factors for MI include coronary artery disease, age, smoking, high blood levels of LDL, low levels of HDL, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, lack of physical exercise, chronic kidney disease, excessive alcohol consumption, and use of illegal drugs (Betts, et al., 2021).
Arrhythmia does not mean an absence of a heartbeat! That would be asystole, or flat line!
Arrhythmia is defined as the absence of a regular rhythm, meaning that the heart rate is either too fast, too slow or just irregular.
The heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node initiates an electrical impulse 60-90 times per minute in a resting adult. This impulse travels through the heart’s conduction system in order to ensure a smooth, coordinated pumping action. This electrical activity can be detected and recorded through the skin using an electrocardiograph. Arrhyhmias may occur when the SA node fails to initiate an impulse, or when the conduction system fails to transmit that impulse through the heart.
In the event that the electrical activity of the heart is severely disrupted, cessation of electrical activity or fibrillation may occur. In fibrillation, the heart beats in a wild, uncontrolled manner, which prevents it from being able to pump effectively.
The most common treatment is defibrillation which uses special paddles to apply a charge to the heart from an external electrical source in an attempt to establish a normal sinus rhythm. A defibrillator effectively stops the heart so that the SA node can trigger a normal conduction cycle. External automated defibrillators (EADs) are being placed in areas frequented by large numbers of people, such as schools, restaurants, and airports. These devices contain simple and direct verbal instructions that can be followed by non-medical personnel in an attempt to save a life (Betts, et al., 2021).
Bradycardia is the condition in which resting adult heart rate drops below 60 bpm. a client exhibiting symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, dizziness, syncope, chest discomfort, palpitations or respiratory distress may indicate that the heart is not providing sufficient oxygenated blood to the tissues. If the patient is not exhibiting symptoms then bradycardia is not considered clinically significant. The term relative bradycardia may be used with a patient who has a HR in the normal range but is still suffering from these symptoms. Most patients remain asymptomatic as long as the HR remains above 50 bpm.
Tachycardia is the condition in which the resting rate is above 100 bpm. Tachycardia is not normal in a resting patient and may be detected in pregnant women or individuals experiencing extreme stress. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic, but when present, symptoms may include dizziness, shortness of breath, rapid pulse, heart palpitations, chest pain, or syncope. Treatment depends upon the underlying cause but may include medications, implantable cardioverter defibrillators, ablation, or surgery (Betts, et al., 2021).
A heart block refers to an interruption in the normal conduction pathway. Heart blocks are generally named after the part of the conduction system that is causing the problem. For example, bundle branch blocks occur within either the left or right atrioventricular bundle branches.
Medical Terms in Context
Cardiologists are medical doctors that specialize in diagnosing and treating heart disease non-invasively. Cardiovascular/thoracic surgeons provide surgical treatments for the heart and other thoracic organs (American Medical Association, 2020). To learn more about these specialists p lease visit the AMA’s Specialty Profiles web page.
Cardiology Technologists complete a college training program and perform diagnostic tests such as electrocardiography, stress testing, Holter monitor testing, ambulatory blood pressure testing, as well as pacemaker monitoring and programming (American College of Cardiology). Please visit the American College of Cardiology webpage for more information.
Cardiovascular perfusionists complete a college training program and are responsible for operation of the heart-lung bypass machine during open heart surgery. They also monitor the patient’s vitals, administering IV fluids, and other drugs (Mayo Clinic). Please visit the Mayo Clinic: Cardiovascular Perfusion page for more information.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Cardiomyopathy. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/cardiomyopathy.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019a). Valvular heart disease. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/valvular_disease.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019b). Aortic aneurysm. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/aortic_aneurysm.htm
[CrashCourse]. (2015, July 6). The heart, part 1 – under pressure: Crash course A&P #25 [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/X9ZZ6tcxArI
Eagleton, M. J. (n.d.). Thoracic aortic aneurysms. Retrieved from Society for Vascular Surgery: https://vascular.org/
Unless otherwise indicated, this chapter contains material adapted from Anatomy and Physiology (on OpenStax), by Betts, et al. and is used under a a CC BY 4.0 international license. Download and access this book for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.
definitionThe number of times the heart contracts in one minute.
× Close definitionThe great vessels include the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, aorta and pulmonary trunk.
× Close definitionThe part of each great vessel (aorta, pulmonary trunk, inferior vena cava, superior vena cava) that connects to the base of the heart
× Close definitionYou may recall that serous membranes throughout the body are folded back on themselves, which results in a double-layered membrane separated by serous fluid. The serous membrane surrounding the lungs is called pleura, The serous membrane surrounding the abdominopelvic organs is called peritoneum.
× Close definitionOne of the two largest veins in the body. It carries deoxygenated blood from the head and upper extremities back to the heart
× Close definitionOne of the two largest veins in the body. It carries deoxygenated blood from the torso and legs back to the heart.
× Close definitionvery large artery referred to as a trunk, a term indicating that the vessel gives rise to several smaller arteries
× Close definitionexcessive development; increase in the size of cells but not the number of cells